Non-Banking Financial
Companies (NBFC)
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a financial institution that provides services like loans, investments, leasing, and insurance, but it doesn’t have a banking license. Unlike banks, NBFCs cannot take savings or current account deposits and don’t deal in agricultural, industrial, or real estate activities as their main business.
To be classified as an NBFC, a company must earn over 50% of its income and hold more than 50% of its assets from financial activities. This rule, called the "50-50 test," ensures that only companies focused mainly on financial services are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Businesses involved in agriculture, trading, or real estate, with limited financial operations, are not considered NBFCs.

The sector is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), with a framework designed to ensure their stability and reliability. RBI’s oversight covers capital adequacy requirements, asset quality, liquidity norms, and corporate governance.
Through periodic updates, RBI has introduced measures to address systemic risks, liquidity management, and consumer protection. For instance, the 2023 RBI Scale-Based Regulations (SBR) established a layered framework that imposes incremental obligations on NBFCs based on their assigned layer. These obligations streamline regulations as NBFCs evolve, taking into account their asset size, scale of activity, and perceived risk level. SBR classifies NBFCs across 4 categories:
01
Base Layer
Smaller NBFCs with minimal systemic risk, including peer-to-peer lending platforms, account aggregators, and entities with limited customer impact. These NBFCs have the least regulatory requirements.
02
Middle Layer
Larger NBFCs, such as deposit-taking entities or those requiring closer supervision. They face stricter regulations on governance, compliance, and risk management due to their scale and potential impact.
03
Upper Layer
Systemically significant NBFCs subject to heightened regulatory standards, including higher capital and risk management requirements akin to banks. These NBFCs are closely monitored for their potential impact on financial stability.
04
Top Layer
NBFCs moved from the upper layer by the RBI when they exhibit a substantial increase in systemic risk.
Types of NBFC
- Asset Finance Company (AFC) Specializes in financing physical assets that support economic activity, such as vehicles, machinery, and industrial equipment.
- Investment Company (IC) Focuses on acquiring and holding securities as its principal business.
- Loan Company (LC) Primarily engaged in providing loans and advances, excluding asset finance activities.
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC) Deploys at least 75% of its total assets in infrastructure loans and maintains a high credit rating and capital adequacy.
- Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI) Provides financial services to low-income individuals, with specific caps on income and loan amounts.
- Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF-NBFC) Facilitates long-term debt flow into infrastructure projects, primarily through bonds.
- Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC-ND-SI) Holds significant investments in group companies’ equity and debt and does not engage in trading.
- NBFC-Factor Focuses on factoring, where receivables constitute at least 50% of its total assets and income.
- Mortgage Guarantee Company (MGC) Offers guarantees on mortgage loans, with at least 90% of its turnover from this business.
- Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC) Acts as a holding entity for setting up a bank and other financial service companies under regulatory supervision.
Compliance is vital for NBFCs to ensure growth, manage risks, and maintain reputation. Adhering to RBI regulations helps mitigate financial risks, build trust, attract investments, and secure long-term stability.
Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including cancellation of registrations by the RBI. Over the past 5 years, RBI cancelled the registrations of 146 NBFCs, demonstrating the significance RBI places on statutory compliance and financial stability.
Penal Measures by RBI
Number of Certificates of Registrations Cancelled and Number of Monetary Penalties levied by RBI over the last 5 years

NBFC Sector Landscape in India
NBFCs Registered with RBI
As of June 2024

- CIC - Core Investment Company
- ICC - Investment and Credit Company
- IDF - Infrastructure Debt Fund
- MFI - Microfinance Institution
- IFC - Infrastructure Finance Company
- Factor - NBFCs engaged in factoring services, which involve purchasing receivables from businesses and managing their collection.
- PD - Primary Dealer
- AA - NBFC-Account Aggregator
- MGC - Mortgage Guarantee Company
- NOFHC - Non-Operative Financial Holding Company
- P2P - Peer-to-Peer Lending Platform
RBI Approvals for NBFCs
Time taken for obtaining critical approvals from RBI

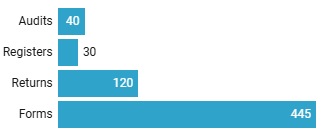
Returns filed with RBI
Unique Returns NBFCs must file with RBI

- RBI requires NBFCs to file statutory returns at fixed frequencies enabling it to keep a close eye on their operations
Core Regulatory Framework for NBFCs in India
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Regulations
- Regulates operations, capital adequacy, and lending norms, ensuring NBFCs’ financial stability and consumer protection.
- Non-compliance can lead to penalties, restrictions on activities, or loss of NBFC license.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Obligations
- Requires stringent verification of clients and transactions to prevent financial crime.
- Failure to comply can result in penalties, reputational damage, and regulatory action.
Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited (CIBIL) Reporting
- NBFCs must report borrower data to maintain a comprehensive credit system.
- Inconsistent or incorrect reporting may impact CIBIL ratings, affecting the NBFC's credibility and customer trust.
Capital Adequacy Requirements (CAR)
- Ensures that NBFCs maintain sufficient capital to absorb potential losses.
- Non-compliance could lead to financial instability and regulatory sanctions.
Fair Practices Code (FPC)
- Mandates transparent and ethical practices in lending, collection, and customer interactions.
- Non-adherence can damage customer trust and result in regulatory scrutiny.
Understanding the Risks of Non-Compliance in NBFC
Importance of Compliance for NBFCs
Customer Protection and Trust
- Compliance with the RBI Act and its subsidiary regulations, directions, circulars, and KYC & AML guidelines is crucial for protecting customers from fraud and financial risks, thereby building trust.
- Non-compliance can lead to customer grievances, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Legal and Financial Risks of Non-Compliance
- Ignoring RBI directives, capital adequacy norms, or fair practices can lead to legal penalties, financial losses, and potential business suspension.
- NBFCs may face fines, legal challenges, and restricted access to capital markets.
Reputation and Market Trust
- Compliance with standards like the Fair Practices Code (FPC) shows a commitment to ethical secure operations.
- Failure in compliance audits or violating customer-centric policies can erode trust, impacting client relationships and partnerships.
Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats
- Non-compliance with data protection standards (such as ISO 27001 for information security) can expose NBFCs to data breaches.
- This not only leads to fines but also damages customer trust and exposes the organization to legal action.
ManuComply: Streamlined Compliance for NBFCs
How ManuComply Simplifies Compliance for NBFCs
- Automated Regulatory Updates: Stay compliant with real-time updates on RBI, KYC/AML guidelines, and other NBFC-specific regulations.
- Audit Readiness: Maintain documentation and records to streamline audits and inspections, such as IS Audits, On-Site and Off-Site Inspections, reducing risk exposure.
- Customizable Workflows: Adapt compliance workflows to support varied operational needs, including customer onboarding, lending, and collections.
- Risk Management and Reporting: Proactively identify gaps in compliance functions and generate comprehensive reports for stakeholders and regulators.

Decoding the Regulatory Framework for a Single Office in One City and State for an NBFC Business
Regulations Prescribing Penalty for Non-Compliance
High Risk - Imprisonment & Monetary Fine; Medium Risk - Monetary Fine; Low Risk - License Revocation

Regulations Prescribing Imprisonment for Non-Compliance

Frequency of Compliance Obligations
Dissecting Unique Annual Compliances across Frequency of their Execution

Break-up of Laws, Rules, and Regulations across Compliance Categories

Break-up of Laws across Levels of Governance

An Illustrative Dissection of Number of Unique Compliance Functions in a Year