FMCG Industry
The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry refers to the sector that manufactures, markets, and sells consumer products that are frequently purchased, relatively low-cost, and quickly consumed. These products typically include:
- Food and Beverages: Packaged foods, snacks, dairy products, and beverages.
- Household Products: Cleaning supplies, detergents, and paper goods.
- Personal Care: Toiletries, cosmetics, and hygiene products.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Pharmaceuticals: Basic health and wellness products.
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector is India’s fourth-largest sector and has been expanding at a healthy rate over the years because of rising disposable income, a rising youth population, and rising brand awareness among consumers.
- Household and personal care products constitute 50% of FMCG sales in India, making the industry a significant contributor to India’s GDP.
- The urban segment accounts for approximately 65% of the total revenue generated by the FMCG sector in India.
- The FMCG market is growing faster in rural India, where FMCG products account for 50% of total spending.

Given the diverse range of products, compliance in FMCG sector is governed by multiple regulations and regulators to ensure consumer safety, product quality, and ethical practices. Key regulatory bodies overseeing the FMCG sector include Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) for food products; Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) and the Consumer Protection Act for quality and safety across goods.
FMCG companies must comply with:
- Labeling norms to provide accurate product information.
- Environmental regulations to promote sustainability.
- Advertising guidelines to prevent misleading claims.
- Packaging requirements to ensure consumer safety and environmental protection.
Compliance is crucial in the FMCG sector to ensure consumer safety, build trust, and meet regulatory requirements. It protects brand reputation, facilitates market access, and supports sustainability goals through ethical and environmentally friendly practices. By adhering to laws and standards, companies avoid legal penalties, minimize risks, and maintain credibility, fostering long-term growth and consumer loyalty.
Overview of the FMCG Industry Landscape
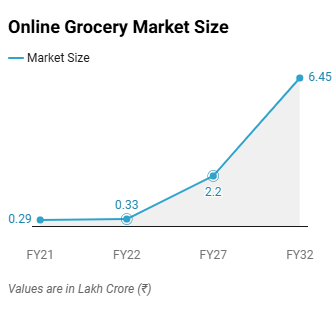
Demand in the FMCG Sector is expected to be driven by increasing semi-urban and rural demand as well as
the rise of e-grocery and online FMCG market.
Core Regulatory Frameworks and Certifications for the
FMCG Industry in India
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) Compliance
- Ensures that food products meet safety, hygiene, and quality benchmarks before reaching consumers.
- Non-compliance can lead to production halts, recalls, fines, and lasting damage to brand reputation.
Legal Metrology Obligations
- Mandates accurate packaging and labeling for consumer transparency, covering product weights, measures, and prices.
- Failure to comply can result in penalties, fines, and a loss of consumer trust.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) Certification
- Establishes standards for quality and safety across various product categories.
- Non-adherence to BIS standards can lead to restricted market access and hindered consumer acceptance.
Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Compliance
- Ensures accurate tax collection and reporting across FMCG supply chains.
- Non-compliance may result in legal issues, penalties, and disruptions in the supply chain.
Environmental Compliance (E-Waste and Plastic Waste Management)
- Regulates the responsible disposal and recycling of packaging materials and electronic waste.
- Non-compliance risks include fines, reputational harm, and restricted operations in environmentally conscious markets.
Understanding the Risks of Non-Compliance in the FMCG Industry
Importance of Compliance for FMCG Companies
Customer Safety and Product Integrity
- Ensures that food products meet safety, hygiene, and quality benchmarks before reaching consumers.
- Non-compliance can lead to production halts, recalls, fines, and lasting damage to brand reputation.
Legal and Financial Risks of Non-Compliance
- Failure to adhere to FSSAI, GST, or environmental regulations can result in legal actions, penalties, and operational shutdowns.
- Non-compliance can affect the company’s bottom line and disrupt operations.
Brand Reputation and Market Trust
- Certifications such as FSSAI and BIS demonstrate a company’s commitment to quality and safety, reassuring consumers and stakeholders.
- Any compliance failure or negative media coverage can harm the brand image, resulting in reduced consumer confidence and loyalty.

ManuComply: Streamlined Compliance for FMCG Companies
How ManuComply Simplifies Compliance for FMCG Companies

Automated
Regulatory Updates
Stay compliant with real-time updates on RBI, Basel III, SEBI, and other regulations.

Audit
Readiness
Keep essential documentation and records organized to streamline audits and regulatory inspections, such as IS Audits, On-Site and Off-Site Inspections, reducing risk exposure.

Customizable
Workflows
Adapt compliance workflows to support a wide range of banking operations, from account onboarding to lending and cybersecurity.

Risk Management
and Reporting
Identify compliance gaps early and generate comprehensive reports for stakeholders and regulators.
Decoding the Regulatory Framework for a FMCG Company with
1 Office and 1 Manufacturing Unit in 1 City in 1 State